Kubernetes/K8s
Kubernetes is the orchestration tool developed by Google to orchestrate the containers in a high availability critical environment.
First of all I would like to explain some important points about Kubernetes which will help you understand this better.
Worker Node
Here are the important components of a Worker Node:
Containers (Pod)
Containers are a completely isolated environment like a VM (Virtual Machine). They will have their own process, networking and mounts but they all share the same operating kernel.
I am sure everyone has heard of container ships where there are a lot of containers which each contain different goods/materials in them.
Let’s assume a server is a container ship and there are multiple containers loaded. This particular server (for example, the container ship) is called a Node Server or a Worker Node. The container (the VM/ application) is called a Pod.
There will be multiple Worker Nodes in a cluster for redundancy purposes (backups in case of failure) and also there will be duplicate applications running in this cluster depending on the usage and for high availability.
2. Node Server
As mentioned before, a server with containers in them is called a Node Server or a Worker Node.
3. Kublets
They are a K8s’ client (service) running on each Node Server in the cluster. They act as a bridge between the pod(container) and the Worker Node, and the Worker Node and the Master Server.
4. Container Runtime Engine
The main purpose of K8s are to orchestrate the containers which run host applications. As everything is based on containers, we need software which will develop the containers; the popular ones include Docker, ContainerD and RKT(Rocket).
Docker is different from Vmware as in Vmware, the ESXi server can run any OS on the VM. But Docker works differently because if the Docker is installed on a linux server, then all the containers have to match the Linux OS. (Cent OS, Suze, Fedora). The advantage is Docker containers boot up faster compared to a VM and they are less isolated as more resources are shared between the containers like the Kernel(platform) due to containerized applications, lower utilization of underlying resources, and Megabytes in size as opposed Gigabytes are results.
5. Kube Proxy
The main job of the Kube Proxy is to make sure the communication between the pods is efficient and reliable. It must be installed in all Worker Nodes. It has intelligent forwarding logic which makes sure the communication happens with low overhead(fewer resources). For example, if the application server needs to send data to the DB server, it will look for a container in the same Worker Node rather than sending it to a different Worker Node, increasing efficiency and decreasing time required.
Now all of the components which are involved in the Worker Node are mentioned above, we will talk about the Master Node.
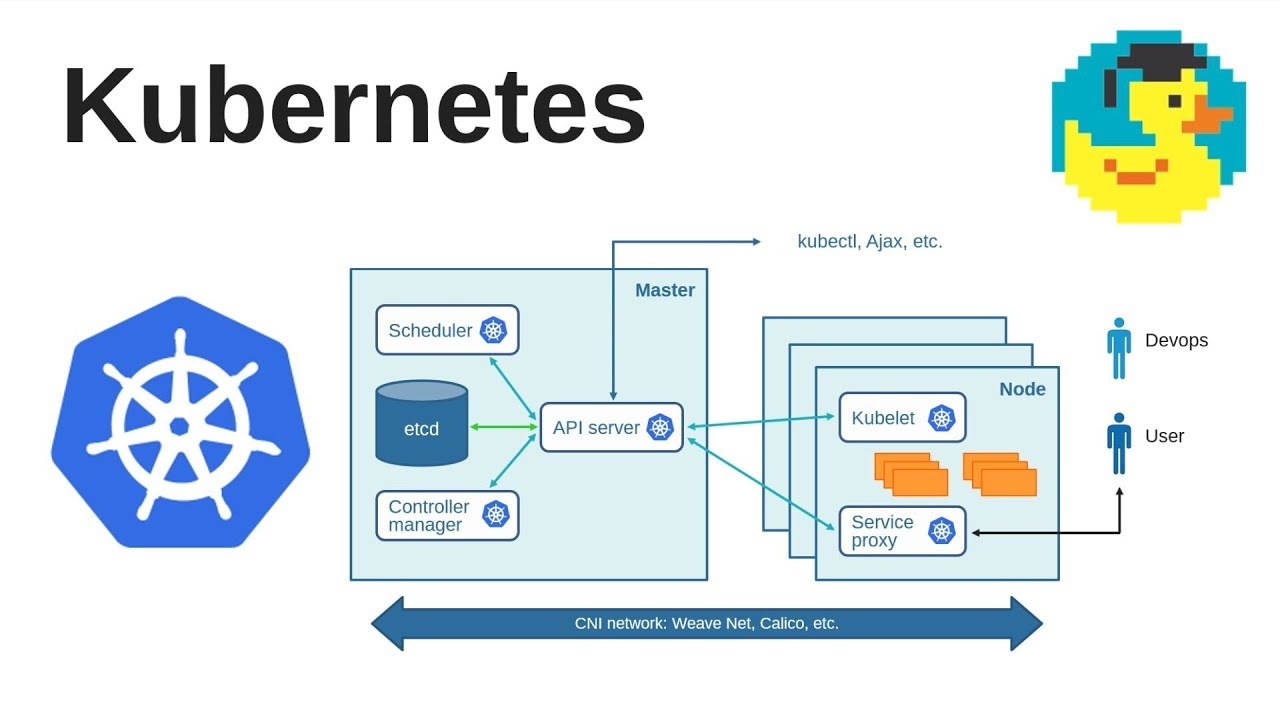
Master Node
The Master Node is the main node which helps to orchestrate the containers running in the Worker Nodes. The Master Node helps to manage, plan, schedule and monitor the nodes.There can be multiple Master nodes in a cluster for redundancy(backup) purposes.
There are 4 main elements of a Master node
- Kube API server
- Kube Scheduler
- Kube Controller Manager
- ETCD Cluster
1. API Server
This is the primary management component. It is responsible for orchestrating all operations within the cluster. It also orchestrates all of the elements in the Master Node. It allows external users to manage operations and make necessary changes to the worker nodes as required.
2. Scheduler
When a new Worker Node is added to the cluster, it is the responsibility of the scheduler to identify where a container should be stored within the different Worker Nodes based on the nodes’ capacities and the container’s resource requirements. Using the example of a container ship, the crane operator moves the containers onto the container ships. It is their responsibility to check the capacity, contents, etc. before loading the containers.
3. Controller Manager
- Node Controller
It takes care of the nodes. It is responsible for onboarding(creating) new nodes and handles when the nodes when they become unavailable or destroyed.
- Replication Controller
This controller makes sure all the containers are running at all times in the replication group(backup).
4. ETCD Cluster
It is a database containing information about the number of containers which are loaded and unloaded on a daily basis. It is important for maintaining information about which containers reside(are stored) in which worker node, and when they were moved. All of this information is stored in a highly available key value store (encrypted database) known as an ETCD.
Minikube
A Minikube is a server with both Master and Worker Nodes installed in it. It is basically used for the testing purposes. In the production environment, there are normally multiple Master Nodes and several Worker Nodes for redundancy, load balancing and high availability purposes. It doesn’t make sense to spend extra resources and time on testing infra in a testing environment, hence Minikube was introduced.
KubeCTL
As mentioned before, the APIServer orchestrates all the elements in the Master and Worker Nodes. External users can make the changes in the cluster with KubeCTL. In addition, all the commands in the K8s start with KubeCTL.
I will be adding more about this topic to this blog, so stay tuned.
